Mother Jones reports: In 2010, a former Wall Street trader flew into war-torn Sudan to negotiate a deal with a thuggish general. He had his eye on a 1 million acre tract of fertile land fed by a tributary of the Nile in the southern section of the country, a region that later claimed its independence as South Sudan. The investor, who planned to profit by developing and exporting agricultural commodities, boasted about how the region’s instability was a principal variable in his financial model: “This is Africa,” he told reporter McKenzie Funk, who shadowed him for a riveting piece in Rolling Stone (PDF). “The whole place is like one big mafia. I’m like a mafia head.”
Over the last decade (and especially during the last four years) wealthy nations have increasingly brokered deals for huge swathes of agricultural land at bargain prices in developing countries, installed industrial-scale farms, and exported the resulting bounty for profit. According to the anti-hunger group Oxfam International, more than 60 percent of these “land grabs” occur in regions with serious hunger problems. Two-thirds of the investors plan to ship all the commodities they produce out of the country to the global market. And droughts, spikes in food and oil prices, and a growing global population have only made the quest for arable land more urgent, and the investments that much more alluring.
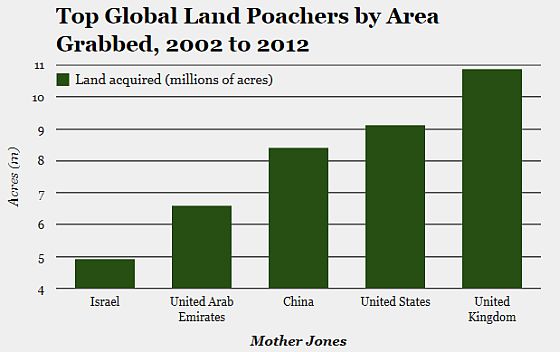
In what a recent study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) characterizes as a “new form of colonialism,” investors from the US, UK, and China are gobbling up foreign farmland at “alarming rates” and often with little consultation and compensation of poor small-scale farmers and local populations. [Continue reading…]

