Editor’s Comment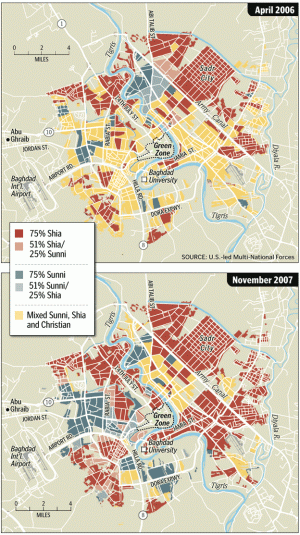 — The good news coming out of Iraq is that most Iraqis see an end to the U.S. occupation as being the key to national reconciliation. The bad news is that the damage done to Iraq’s social frabric over the last five years is going to be extremely difficult to repair. The problem is starkly depicted in these two maps of Baghdad. In the space of eighteen months, the city has transformed from being predominently made up of mixed neighborhoods (depicted in yellow), to being sharply divided between Shia and Sunni sectors. Now, colliding with this division are returning refugees:
— The good news coming out of Iraq is that most Iraqis see an end to the U.S. occupation as being the key to national reconciliation. The bad news is that the damage done to Iraq’s social frabric over the last five years is going to be extremely difficult to repair. The problem is starkly depicted in these two maps of Baghdad. In the space of eighteen months, the city has transformed from being predominently made up of mixed neighborhoods (depicted in yellow), to being sharply divided between Shia and Sunni sectors. Now, colliding with this division are returning refugees:
A small fraction of the millions of refugees who fled Iraq have come back. While the government trumpeted their return as proof of newfound security, migration experts said most of them were forced back by expired visas and depleted savings…
The American military has expressed deep concerns about the Iraqi government’s ability to feed and house its returnees, or manage people who wish to reclaim their homes. It is widely feared that property disputes or efforts to return to newly homogenized neighborhoods could set off fresh waves of sectarian attacks.
For most Iraqi refugees, the trip home is just the beginning of their troubles. Many return to find their homes destroyed or filled with squatters, most of them displaced people themselves. But the government committee that decides property disputes is charged with hearing only cases that predate the invasion of 2003.
Strategy that is making Iraq safer was snubbed for years
[A] USA TODAY investigation shows that the strategy now used to defeat the bombmaking networks and stabilize Iraq was ignored or rejected for years by key decision-makers. As early as 2004, when roadside bombs already were killing scores of troops, a top military consultant invited to address two dozen generals offered a “strategic alternative” for beating the insurgency and IEDs.
That plan and others mirroring the counterinsurgency blueprint that the Pentagon now hails as a success were pitched repeatedly in memos and presentations during the following two years, at meetings that included then-Defense secretary Donald Rumsfeld, Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice and Vice President Cheney’s chief of staff, Lewis “Scooter” Libby.
The core of the strategy: Clear insurgents from key areas and provide security to win over Iraqis, who would respond by helping U.S. forces break IED networks and defeat the insurgency.
Bush administration officials, however, remained wedded to the idea that training the Iraqi army and leaving the country would suffice. Officials, including Cheney, insisted the insurgency was dying. Those pronouncements delayed the Pentagon from embracing new plans to stop IEDs and investing in better armored vehicles that allow troops to patrol more freely, documents and interviews show.
Even after the Pentagon began committing substantial resources to combat IEDs, USA TODAY found, its spending focused mostly on high-tech devices with limited utility. Some silver-bullet solutions, such as microwave beams designed to destroy IEDs before they blew up, never worked.
By the time the Pentagon moved to a counterinsurgency strategy at the end of last year, the bombs had been the top killer of U.S. troops for three years, claiming more than 1,160 lives. To date, they are responsible for more than 60% of combat deaths. [complete article]


In the lead up to invading Iraq, the Bush administration implied that the post-invasion phase of Iraq would be fairly straight forward and would essentially take care of itself. This article suggests this wasn’t merely a cynical ploy to sell the invasion to the American public – Bush and his top advisors genuinely believed it, and continued to believe it up until the end of 2006.